Repurchase Agreements (Repo) is a money market instrument, which enables co-lateralised short term borrowing and lending through sale/purchase operations in debt instruments.
Under a repo transaction, a holder of securities sells them to an investor with an agreement to repurchase at a predetermined date and rate. In the case of a repo, the forward clean price of the bond is set in advance at a level which is different from the spot clean price by adjusting the difference between repo interest and coupon earned on the security.
In the money market, this transaction is nothing but co-lateralised lending as the inflow of cash from the transaction can be used to meet temporary liquidity requirement in the short term money market at comparable cost.
A Repurchase Agreements (Repo) is also sometimes called a ready forward transaction as it is a means of funding by selling a security held on a spot (ready) basis and repurchasing the same on a forward basis.
When an entity sells a security to another entity on repurchase agreement basis and simultaneously purchases some other security from the same entity on resale basis it is called a double ready forward transaction.
Read Also: What is repo rate?
Reverse Repo
A reverse repo is the mirror image of a repo. For, in a reverse repo, securities are acquired with the simultaneous commitment to resell. Hence, whether a transaction is a repo or a reverse repo is determined only in term of who initiated the first leg the transaction. When the reverse repurchase transaction matures, the counter-party returns the security to the entity concerned and receives its cash along with the profit spread. One factor which encourages an organisation to enter into reverse repo is that it earns some extra income on its otherwise idle cash.
Repurchase Agreements (Repo) Period
Repurchase Agreements (Repo) period could be overnight, term, open or flexible. Overnight reports last only one day. If the period is fixed and agreed in advance it is a term repo where either party may call for the repo to be terminated at any time although requiring one or two days’ notice. Though there is no restriction on the maximum period for which repo can be undertaken generally term repo are for an average period of one week. In an open repo, there is no such fixed maturity period and the interest rate would change from day to day depending on the money market conditions.
Types of Repos
Broadly, there are four types of Repurchase Agreements (Repo) available in the international market when classified with regard to maturity of underlying securities, pricing, term of repo etc. They comprise buy-sell back repo, classic repo, bond borrowing and lending and tripartite repo.
-
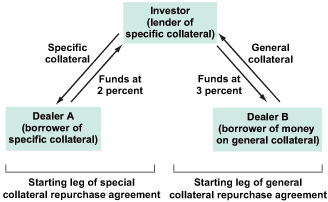
Buy-Sell Back Repo – Under a buy-sell repo transaction the lender actually takes the position of the collateral. Here a security is sold outright and brought back simultaneously for settlement on a later date. In a buy-sell repo, the ownership is passed on to the buyer and hence, he retains any coupon interest due on the bonds. The spot buyer/borrower of securities in effect earns the yield on the underlying security plus or minus difference between these and the repo interest rate.
-
Classic Repo – Is an initial sale of securities with a simultaneous agreement to repurchase them at a later date. In the case of this type of repo the start and end prices of the securities are the same and the separate payment of “interest” is made.
-
Bond Lending/Borrowing – In a bond lending/borrowing transaction, the customer lend bonds for an open-ended or fixed period in return for a fee. The fee charged would depend on the type of underlying instrument, size and term of the loan and the credit rating of the counterparty. The transaction would be taken care of by an agreement on securities lending and cash or other securities of equal value could be provided as collateral in the transaction.
-
Tripartite repo – Under a tripartite repo, a common custodian/clearing agency arranges for custody, clearing and settlement of repo transactions. They operate under a standard global master purchase agreement and provides for DVP system, substitution of securities, automatic marking to market, reporting and daily administration by the single agency.
This type of arrangement minimises credit risk and can be utilized when dealing with clients with low credit rating.
Also, Read: