National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development is set up as an apex Development Bank with a mandate for facilitating credit flow for promotion and development of agriculture, small-scale industries, cottage and village industries, handicrafts and other rural crafts. It also has the mandate to support all other allied economic activities in rural areas, promote integrated and sustainable rural development and secure prosperity of rural areas. In discharging its role as a facilitator for rural prosperity National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development is entrusted with
- Providing refinance to lending institutions in rural areas
- Bringing about or promoting institutional development and
- Evaluating, monitoring and inspecting the client banks
Read Also: Solid Waste Management (SWM) : Growing for Solutions
Besides this pivotal role, National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development also:
- Acts as a coordinator in the operations of rural credit institutions
- Extends assistance to the government, the Reserve Bank of India and other organizations in matters relating to rural development
- Offers training and research facilities for banks, cooperatives and organizations working in the field of rural development
- Helps the state governments in reaching their targets of providing assistance to eligible institutions in agriculture and rural development
- Acts as regulator for cooperative banks and RRBs
- Extends assistance to the government, the Reserve Bank of India and other organizations in matters relating to rural development
- Offers training and research facilities for banks, cooperatives and organizations working in the field of rural development
- Helps the state governments in reaching their targets of providing assistance to eligible institutions in agriculture and rural development
- Acts as regulator for cooperative banks and RRBs
Read Also: Few Facts About Reserve Bank of India
Some of the milestones in National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development’s activities are:
- Total production credit disbursed at end March 2011 was 34196 crore.
- Refinance disbursement under Investment Credit to commercial banks, state cooperative banks, state cooperative agriculture and rural development banks, RRBs, and other eligible financial institutions during 2010-11 aggregated 13485.87 crores.
- Through the Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF) 12060.04 crores were disbursed during 2010-11. A cumulative amount of 121488.40 crores has been sanctioned for 444162 projects as on 31 March 2011 covering irrigation, rural roads, and bridges, health and education, soil conservation, drinking water schemes, flood protection, forest management etc.
- Under Watershed Development Fund which has a balance of 1847.69 crores as on 31 March 2011, 579 projects in districts of 14 states have benefited.
- Farmers now enjoy hassle free access to credit and security through 1009.30 lakh Kisan Credit Cards that have been issued through a vast rural banking network. During 2010-11, 72.6 lakh KCC were issued by banks with a sanctioned limit of 43370 crores.
- Under the Farmers’ Club Programme, during the year 21903 clubs were launched, taking the total to 76708 clubs as on 31 March 2011 helping farmers get access to credit, technology and extension services.
- Village Development Programme (VDP) is being implemented in 801 villages across 25 states.
- Under Tribal Development Fund, cumulative sanction amounted to 917.60 crores for 317 projects covering 2.5 lakh families. During 2010-11 financial assistance of 373.97 crores was sanctioned for 126 projects benefiting 94,163 tribal families.
- Under Farm Innovation and Promotion Fund (FIPF), cumulatively 123 projects in various states, involving financial support of 11.65 crores were sanctioned as on 31 March 2011.
- Farmers Technology Transfer Fund (FTTF) – 512 innovative projects in 27 states with grant assistance of 44.97 crores were sanctioned during 2010-11.
- There were more than 69.53 lakh savings linked SHGs and more than 48.51 lakh credit linked SHGs covering 9.7 crore poor households as on 31 March 2011, under the microfinance programme.
Don’t Miss: NABARD Collaborates with Germans on SPRFS
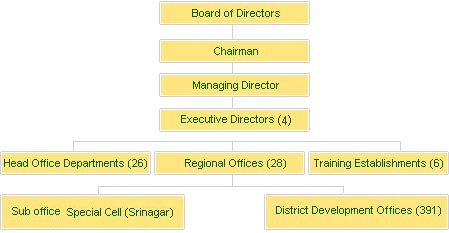
Organisational Structure of NABARD:
Reference: Official NABARD Website
Also, Read:
PM Ujjwala Yojana: an LPG Scheme
Digital India (DI) Project : A Mission
Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT)