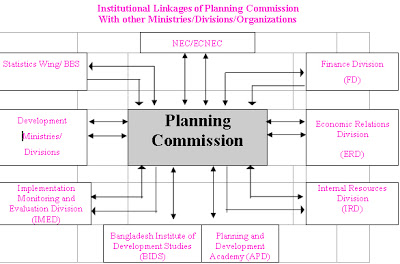
Planning Commission of India
Planning Commission of India was an institution in the government of India, which formulated India’s Five-Year-Plans, among other functions.
There is no account of Planning Commission of India in the Indian Constitution. Therefore, it was constituted in the form of an advisory and specialised institution by means of a document of Government. Consequently, the Government has been changing its nature and organisation from time to time.
The Prime Minister Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru was appointed the first Chairman of Planning Commission, 5 full-time members were also nominated. The ministers and scholars have been nominated in this commission from time to time, the Prime Minister remains its ex-officio Chairman. The tenure of its members and Vice Chairman is not fixed. There is no definite qualification for its members. The members are appointed by Government for its own discretion. The number of its members keep on changing according to the wish of the Government.
Functions of the Planning Commission
1. To estimate the physical, capital and human resources of the country.
2. To prepare the plan for making effective and balanced utilisation of human resource.
3. To determine the various stages of planning and to propose the allocation of resources on the priority basis.To indicate those factors to the Government which proves an obstacle
4. To indicate those factors to the Government which prove an obstacle for the economic development and also to determine those circumstances which are necessary for the implementation of the plans under existing social and political situation.
5. To evaluate from time to time the progress achieved in every stage of the plan and also to suggest remedial measures.
6. To advice, the Centre and the State Government on special matters referred to the commission.
Related Posts:
History of Planning Commission in India
Terms Pertaining to Government
Central Vigilance Commission (CVC)