Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Historical Background and Motivation
- Why Use Feynman Diagrams?
- Perturbation Theory in QFT
- Building Blocks of Feynman Diagrams
- Feynman Rules Overview
- External Lines and Particle States
- Propagators
- Vertices and Coupling Constants
- Conservation Laws at Vertices
- Internal Lines and Virtual Particles
- Example: Electron-Photon Scattering (Compton Scattering)
- Fermion Loops and Anomalies
- Symmetry Factors and Diagram Counting
- Renormalization and Loop Corrections
- Cross Sections and Amplitudes
- Dimensional Analysis and Power Counting
- Limitations of Feynman Diagrams
- Beyond Tree-Level: Loop Diagrams
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
Feynman diagrams are pictorial representations of the mathematical expressions describing interactions between particles in quantum field theory (QFT). Introduced by Richard Feynman, they serve as intuitive tools for computing amplitudes in perturbation theory.
2. Historical Background and Motivation
Developed in the 1940s, Feynman diagrams revolutionized QED calculations, making complex interactions between particles more manageable. They provide both physical insight and calculational rigor, underpinning much of modern particle physics.
3. Why Use Feynman Diagrams?
- Visualize particle interactions
- Systematically organize terms in perturbation theory
- Represent quantum amplitudes and probabilities
- Simplify computation of cross sections and decay rates
4. Perturbation Theory in QFT
QFT observables are expanded in powers of the coupling constant (e.g., \( \alpha \) in QED):
\[
\mathcal{M} = \mathcal{M}^{(0)} + \mathcal{M}^{(1)} + \mathcal{M}^{(2)} + \cdots
\]
Each term corresponds to a diagram with increasing number of vertices and loops.
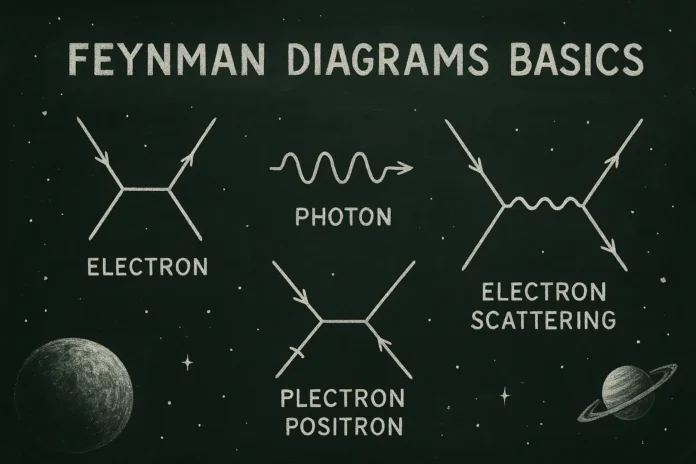
5. Building Blocks of Feynman Diagrams
Feynman diagrams consist of:
- External lines: incoming/outgoing particles
- Internal lines: propagators of virtual particles
- Vertices: interaction points (e.g., \( e\bar{\psi}\gamma^\mu A_\mu\psi \))
6. Feynman Rules Overview
Feynman rules translate diagrammatic elements into mathematical expressions. Rules differ by theory (e.g., QED, QCD), but generally include:
- Assign momenta to each internal line
- Use vertex factors, propagators, and spinors
- Integrate over internal momenta
7. External Lines and Particle States
- Represent real particles entering/leaving interaction
- Associated with wavefunctions:
- \( u(p) \), \( \bar{u}(p) \) for electrons
- \( v(p) \), \( \bar{v}(p) \) for positrons
- \( \epsilon^\mu(k) \) for photons
8. Propagators
Represent internal virtual particles:
- Photon:
\[
\frac{-i\eta^{\mu\nu}}{k^2 + i\epsilon}
\] - Electron:
\[
\frac{i(\not{p} + m)}{p^2 – m^2 + i\epsilon}
\] - Scalar:
\[
\frac{i}{p^2 – m^2 + i\epsilon}
\]
9. Vertices and Coupling Constants
Each vertex contributes a factor:
- QED vertex: \( -ie\gamma^\mu \)
- Scalar QFT: \( -i\lambda \)
Number of vertices = order of perturbation theory.
10. Conservation Laws at Vertices
At each vertex:
- 4-momentum is conserved.
- Charge and other quantum numbers are conserved.
This ensures the physical consistency of the theory.
11. Internal Lines and Virtual Particles
- Internal lines correspond to virtual particles.
- They are not observed directly.
- They do not obey the usual energy-momentum relation \( E^2 = p^2 + m^2 \).
12. Example: Electron-Photon Scattering (Compton Scattering)
Two leading-order diagrams:
- s-channel: photon absorbed and re-emitted by the same electron
- u-channel: final photon emitted before absorbing the initial one
Each diagram corresponds to a distinct mathematical term.
13. Fermion Loops and Anomalies
Loops involving fermions appear in higher-order corrections:
- Vacuum polarization
- Self-energy diagrams
- Triangle anomalies (important in gauge theory consistency)
14. Symmetry Factors and Diagram Counting
Some diagrams contribute multiple times due to symmetries:
- A factor of \( \frac{1}{2} \) or more may be applied
- Ensures correct weight in the perturbation expansion
15. Renormalization and Loop Corrections
Loop diagrams often diverge:
- Require regularization (e.g., dimensional regularization)
- Renormalization removes infinities and defines finite physical parameters
16. Cross Sections and Amplitudes
The scattering amplitude \( \mathcal{M} \) is computed from diagrams:
\[
\frac{d\sigma}{d\Omega} \propto |\mathcal{M}|^2
\]
All relevant diagrams must be included up to a given order.
17. Dimensional Analysis and Power Counting
- Determines which diagrams contribute most at low or high energies.
- Aids in effective field theory and understanding UV/IR behavior.
18. Limitations of Feynman Diagrams
- Only valid in weakly coupled theories
- Complicated for non-abelian gauge theories (e.g., QCD)
- Do not manifestly preserve unitarity or Lorentz invariance in all formulations
19. Beyond Tree-Level: Loop Diagrams
- Tree-level: no loops, simplest approximation
- 1-loop, 2-loop, etc.: higher precision but more complexity
- Necessary for precision tests and anomaly calculations
20. Conclusion
Feynman diagrams are indispensable tools in quantum field theory. They provide both a visual and algebraic language to describe particle interactions, enabling physicists to compute observables and predict physical phenomena. A deep understanding of Feynman diagrams is essential for advanced work in particle physics and quantum field theory.